Appearance
Clump Modifier
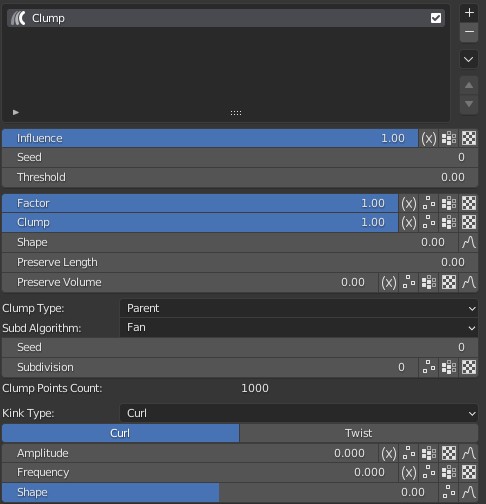
Modifier Options
Factor: Controls the strength of the Clump modifier overall. When it is 0, the modifier doesn't work.
Clump: It works similarly to the Clump under Clumping.
Shape: It works similarly to Shape under Clumping, and it can be flexibly controlled by a Curve.
Preserve Length: Maintain the length of the hair after clumping. When it is set to 0, hair will be stretched to a point. When it is set to 1, hair keeps its original length.
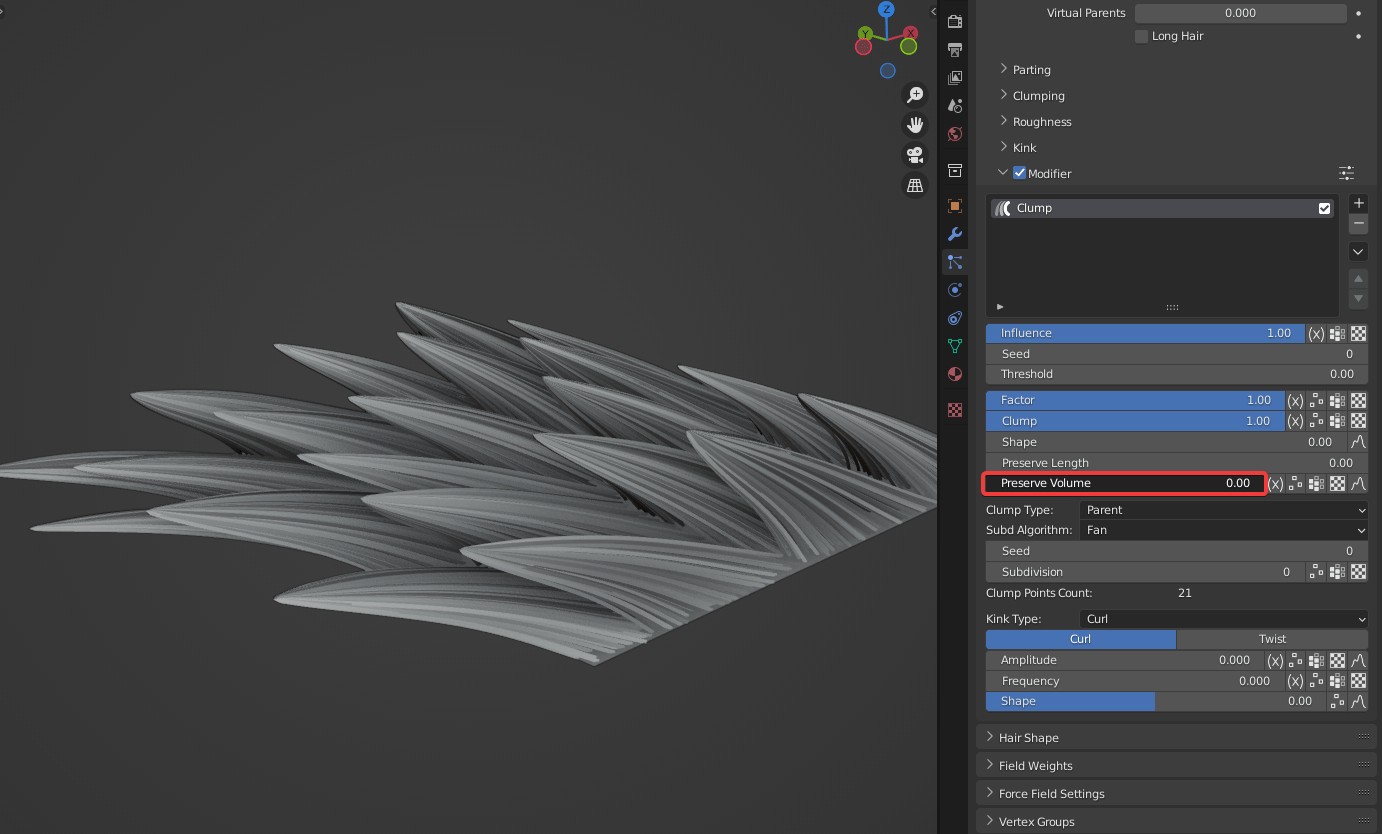
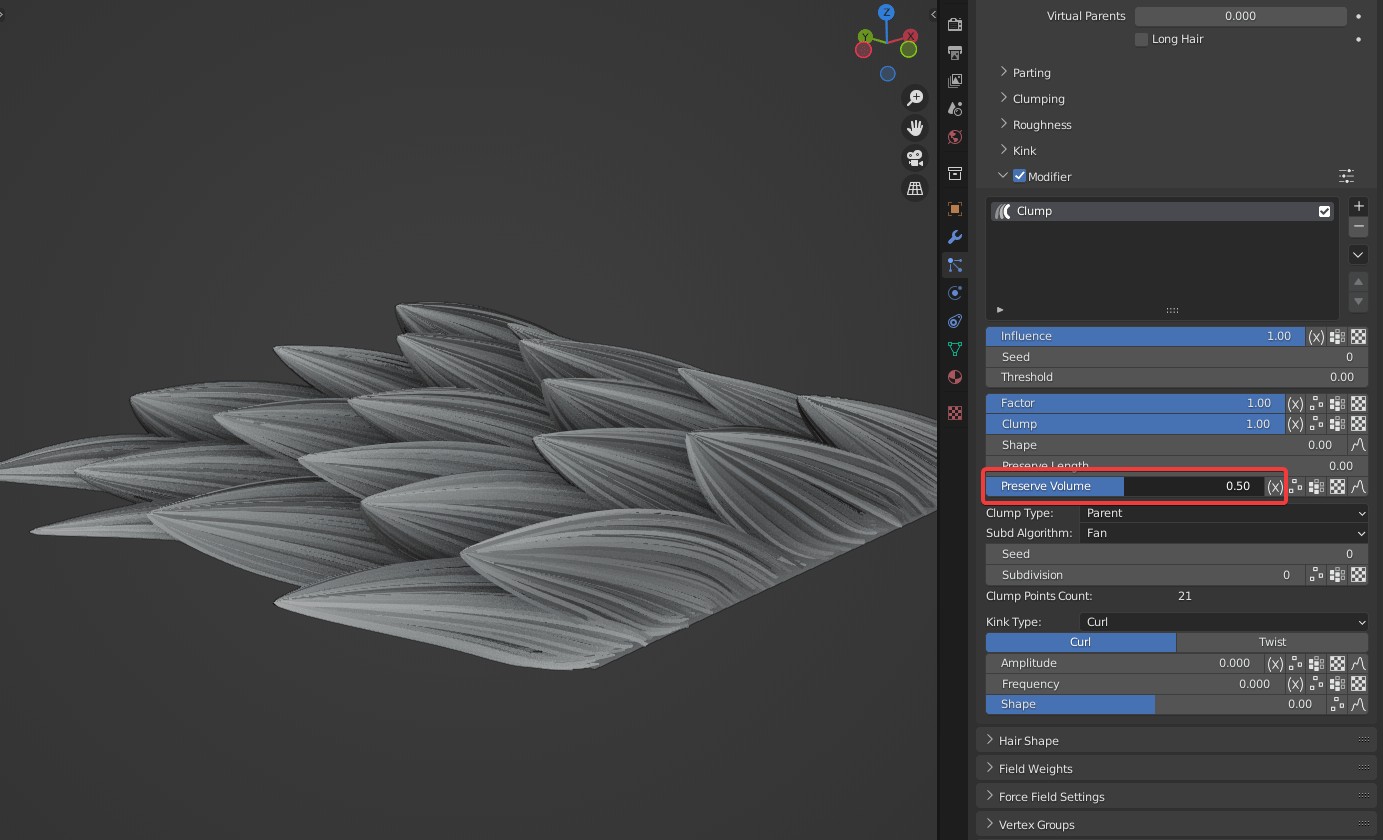
Preserve Volume: Controls volume of hair roots after clumping.
Clump Type
Two clumping algorithms are available for different needs: Parent and Generated.
In Parent mode, Clumping is generated based on parent, so Subdivision cannot be smaller than the number of parents.
In Generated mode, the number of clumps is not limited by the number of parents. Clumps are generated by nearby Children on the surface randomly.
Parent
TIP
Tip: It's better to apply Parent mode when the number of existing clumps is small. The calculation is fast.
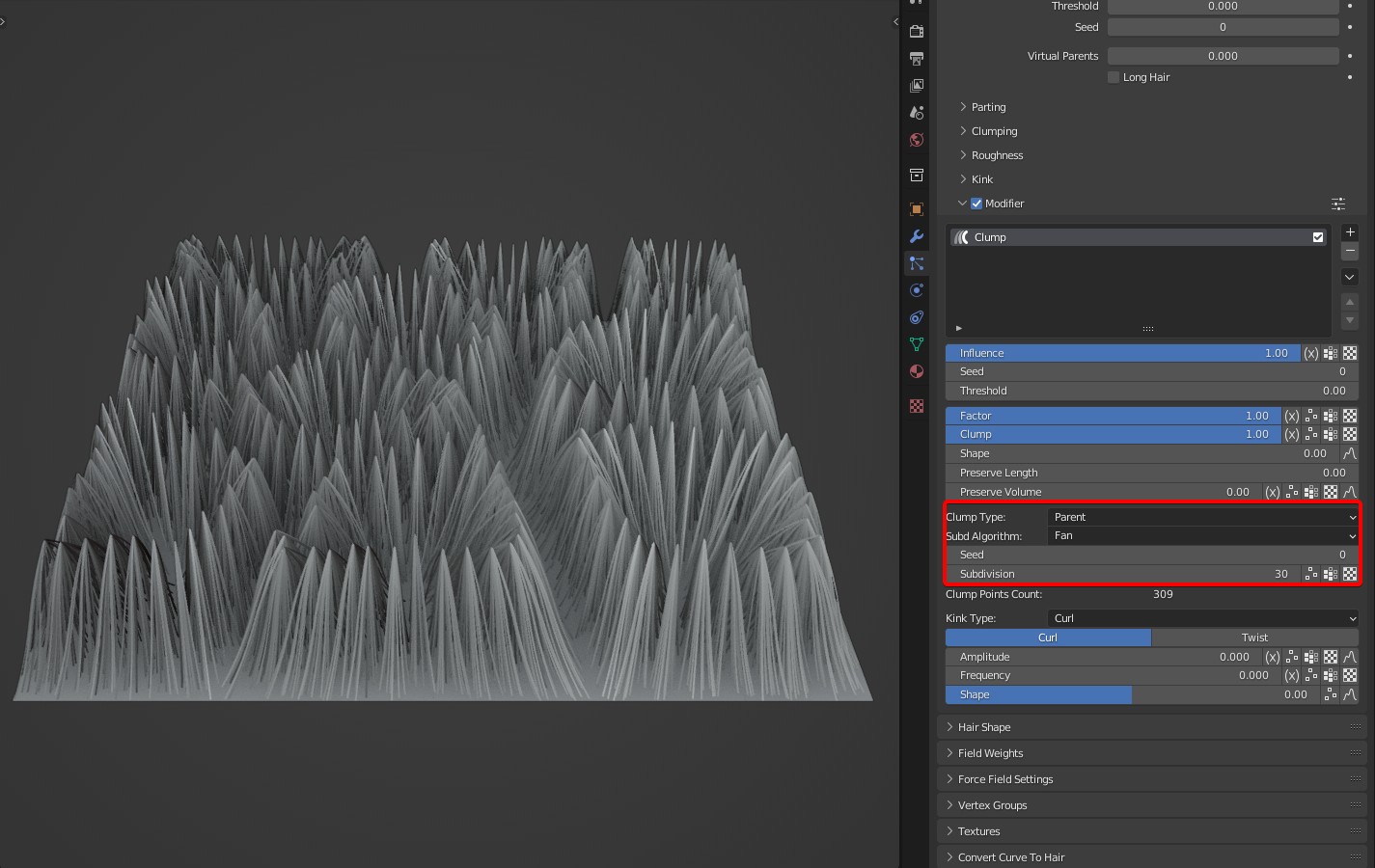
Subd Algorithm: Calculation of subdivision. Two algorithms are available: Fan and Random.
- Fan is a fan-shaped bisection of a parent clump. It will be very obvious when children Simple is applied.
Unsubdivided effect
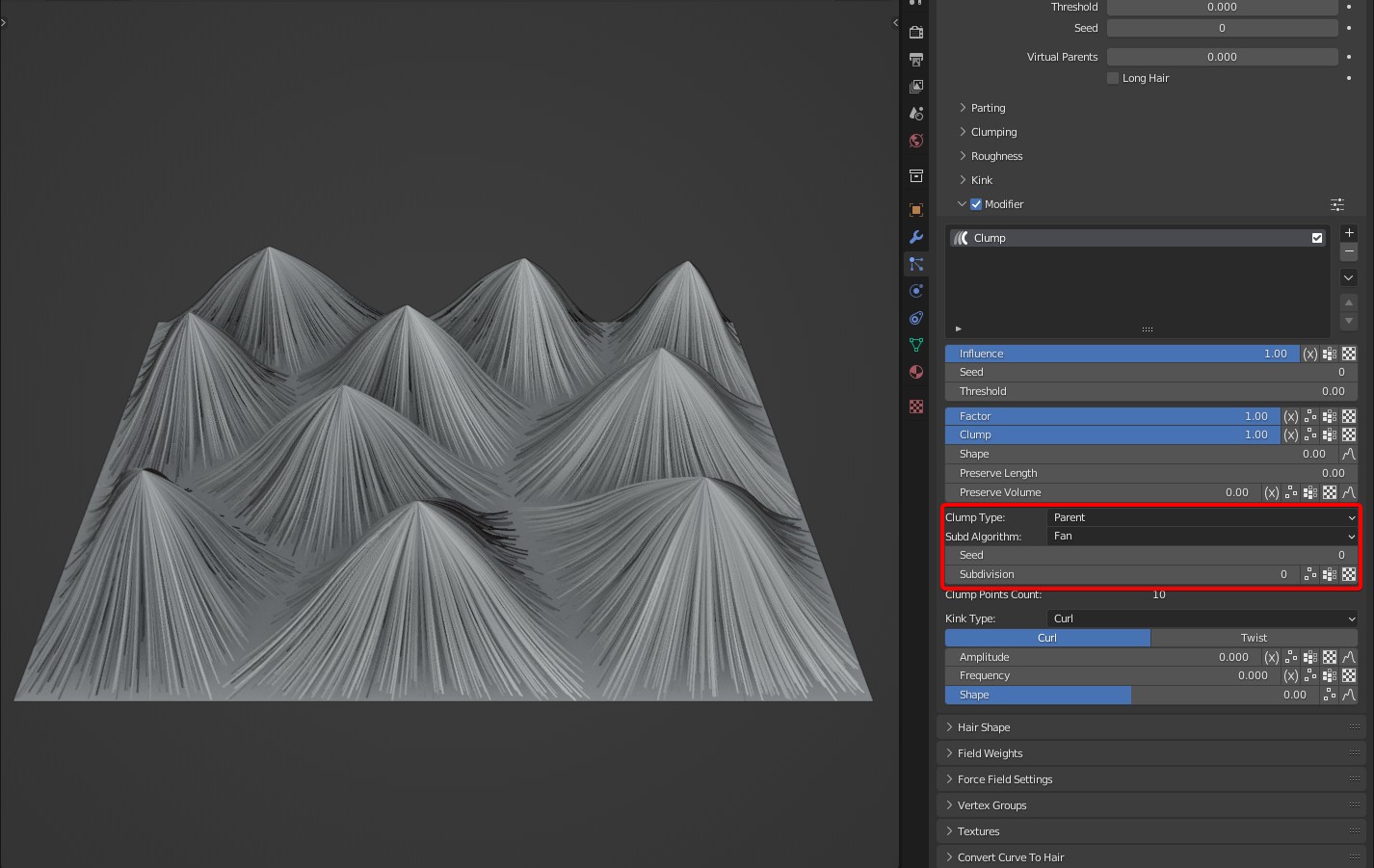
Fan effect
- In Random mode, clumping is not as rigid as the effect in Fan mode, and it can soften the rigid demarcation.
Unsubdivided effect
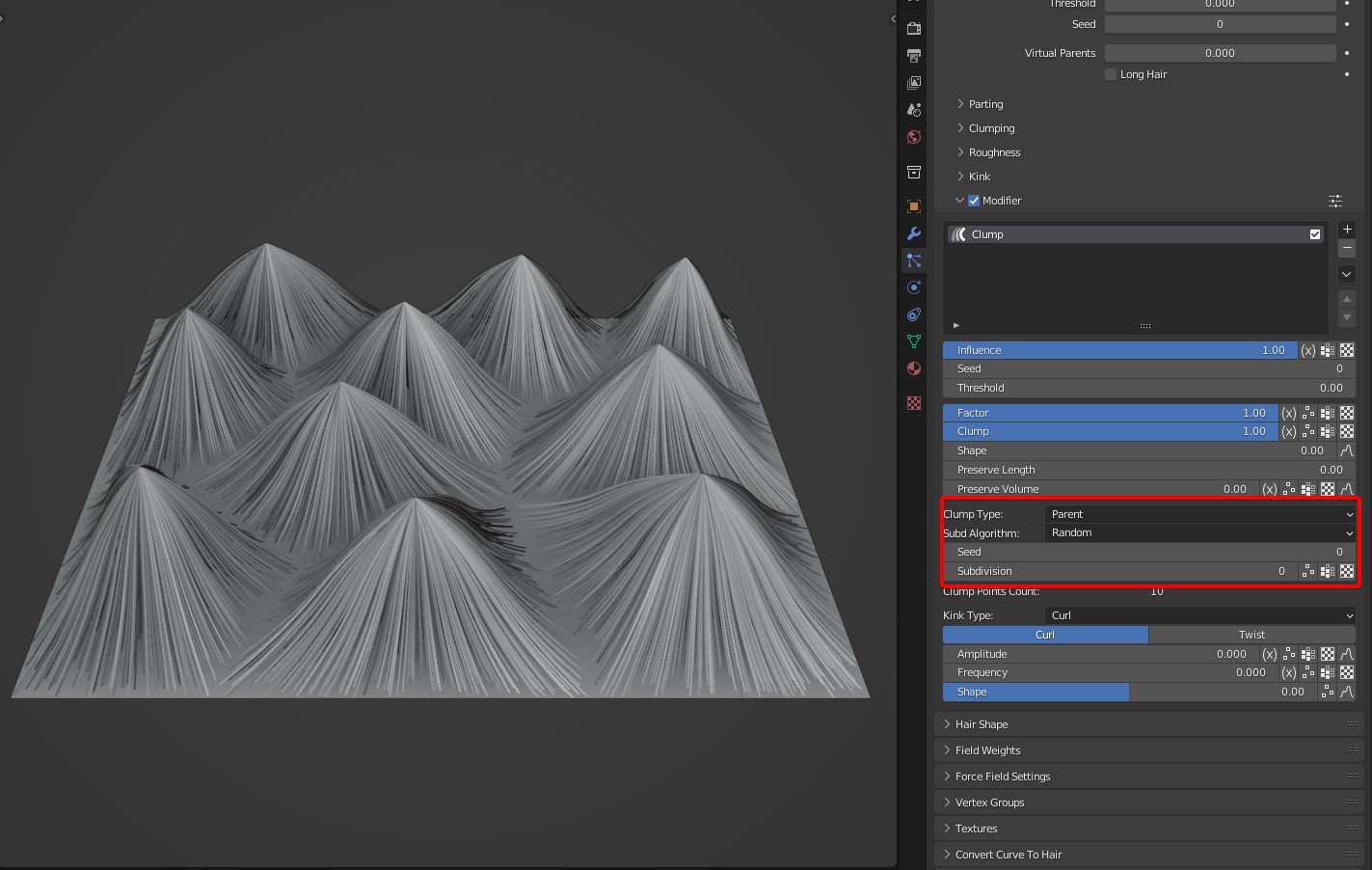
Random effect
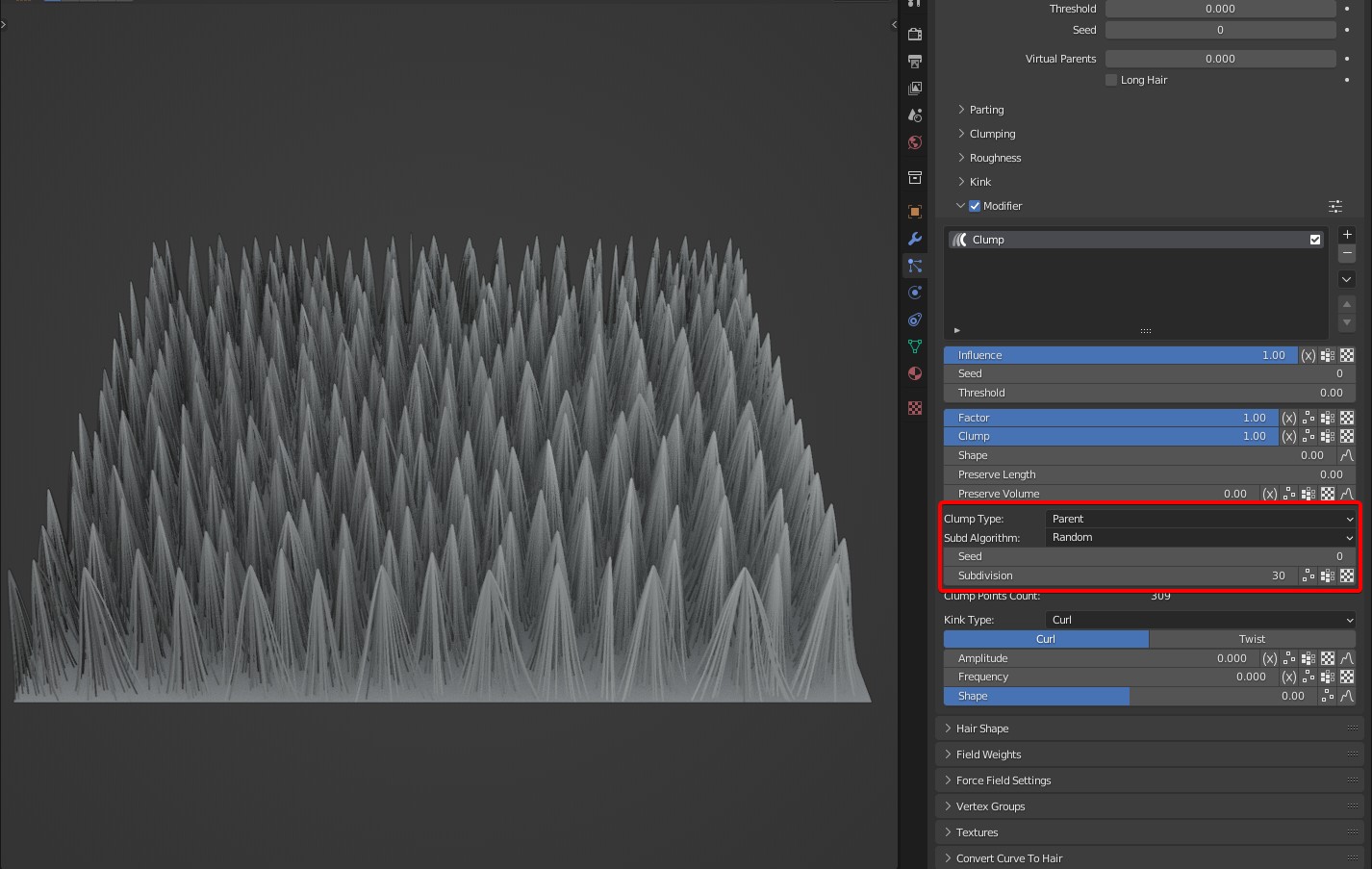
Seed: Randomize the position where the clumps are.
Subdivision: The time of subdivision of clumps.
Generated
TIP
Tip: In this mode, the number of clumps is not limited by the number of parents. It works well when a small number of clumps are required. But calculation is relatively slow, especially when density is high.
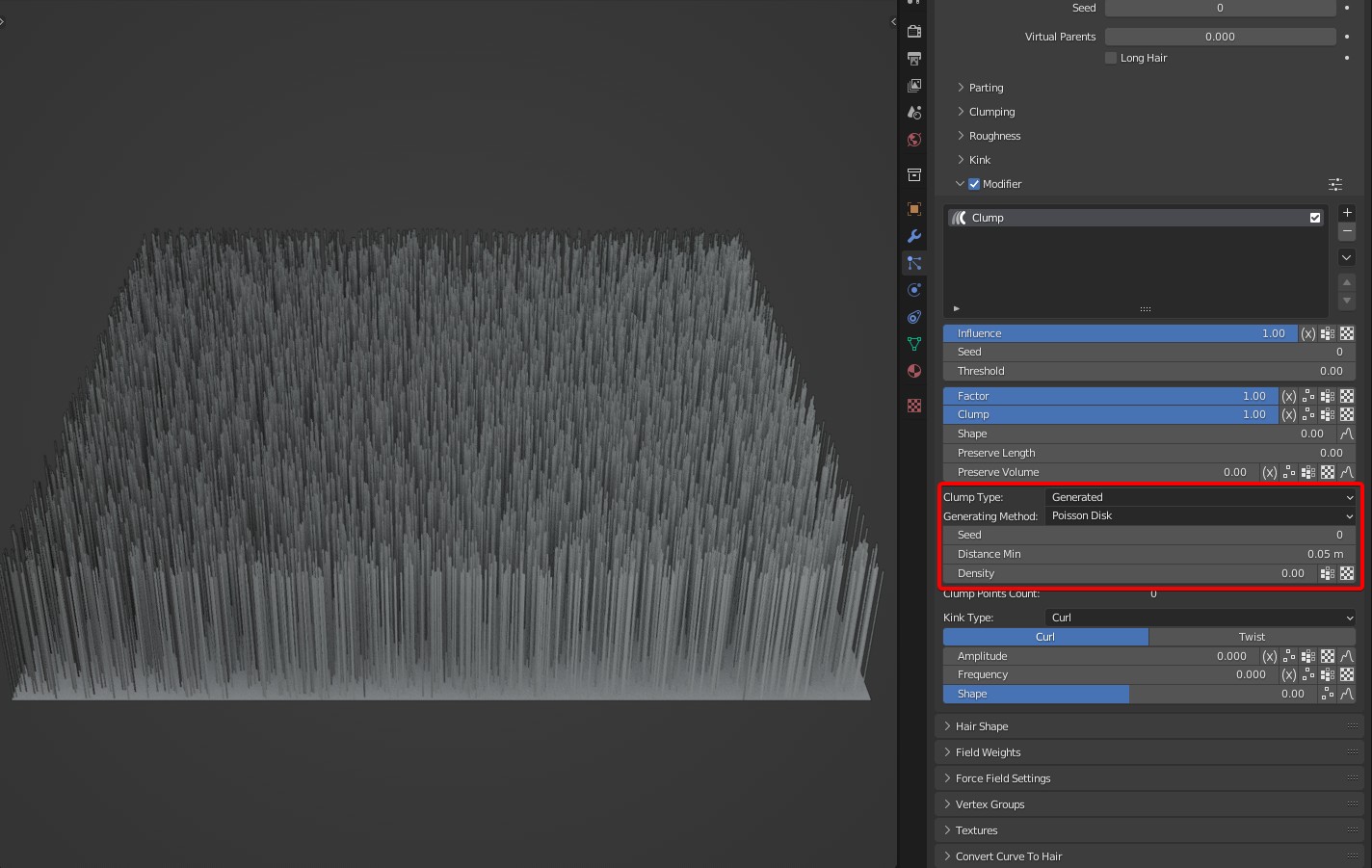
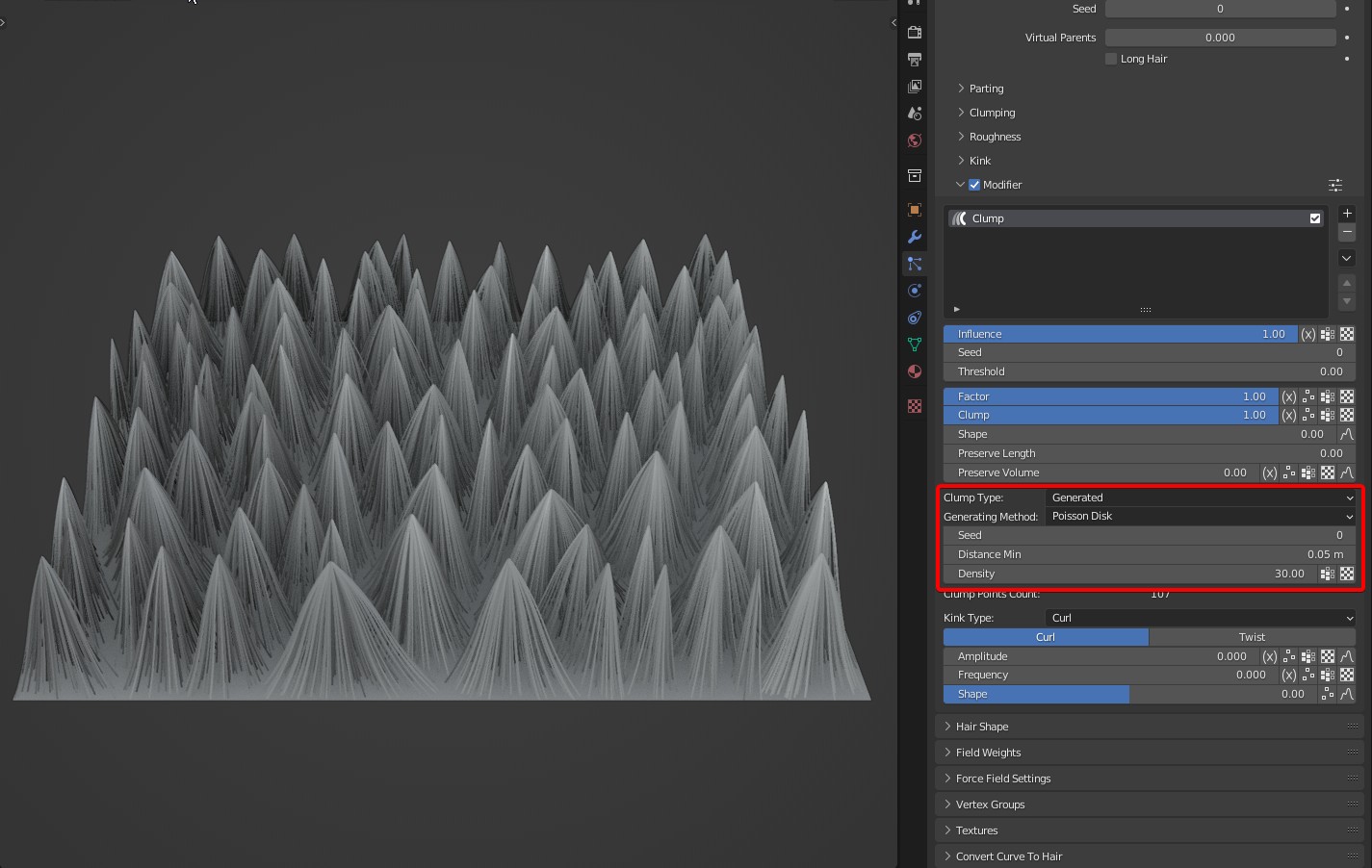
Generating Method: Two algorithms are available: Grid and Poisson Disk.
- Grid: The generated clump points are evenly distributed. The higher the density, the slower the speed.
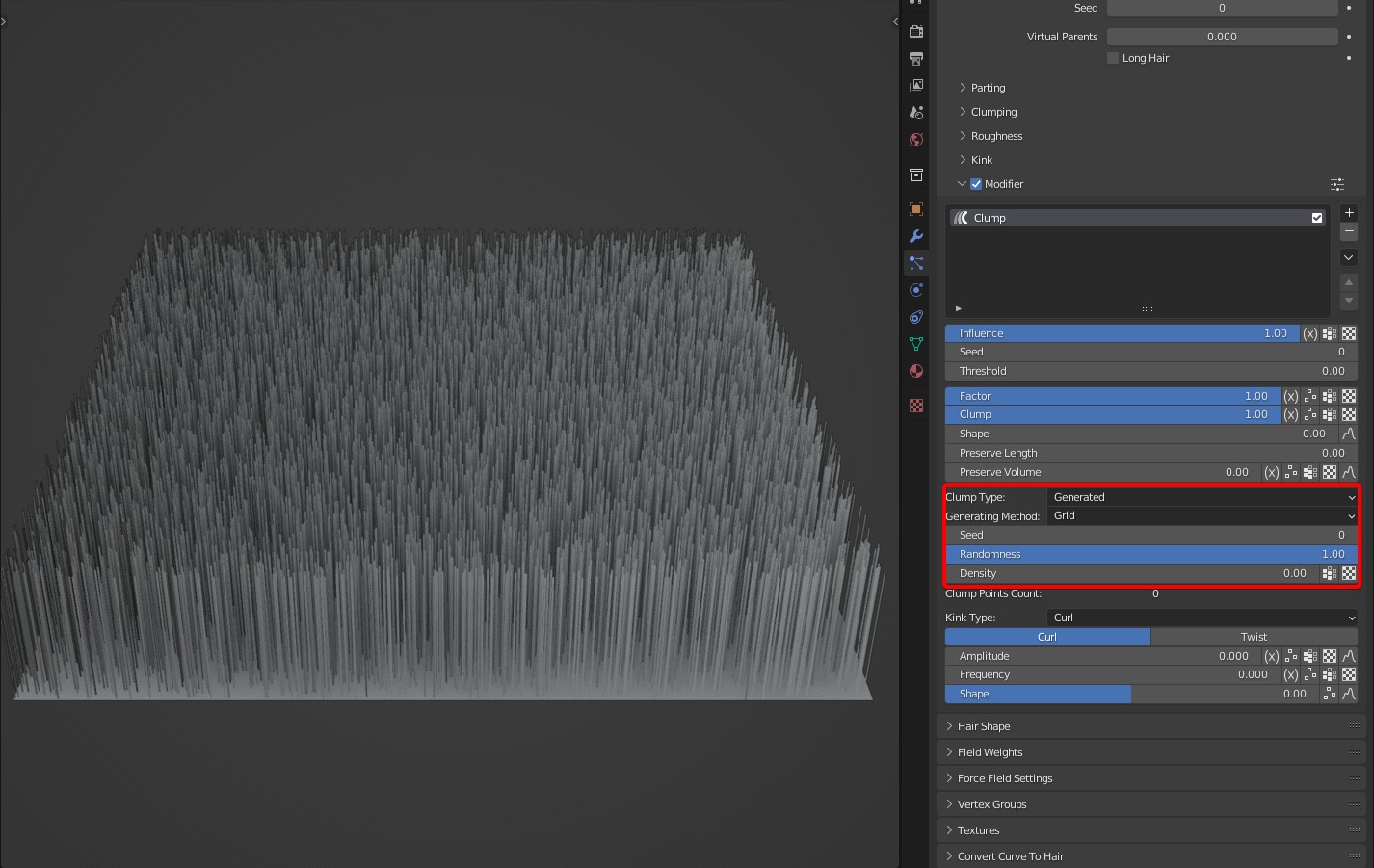
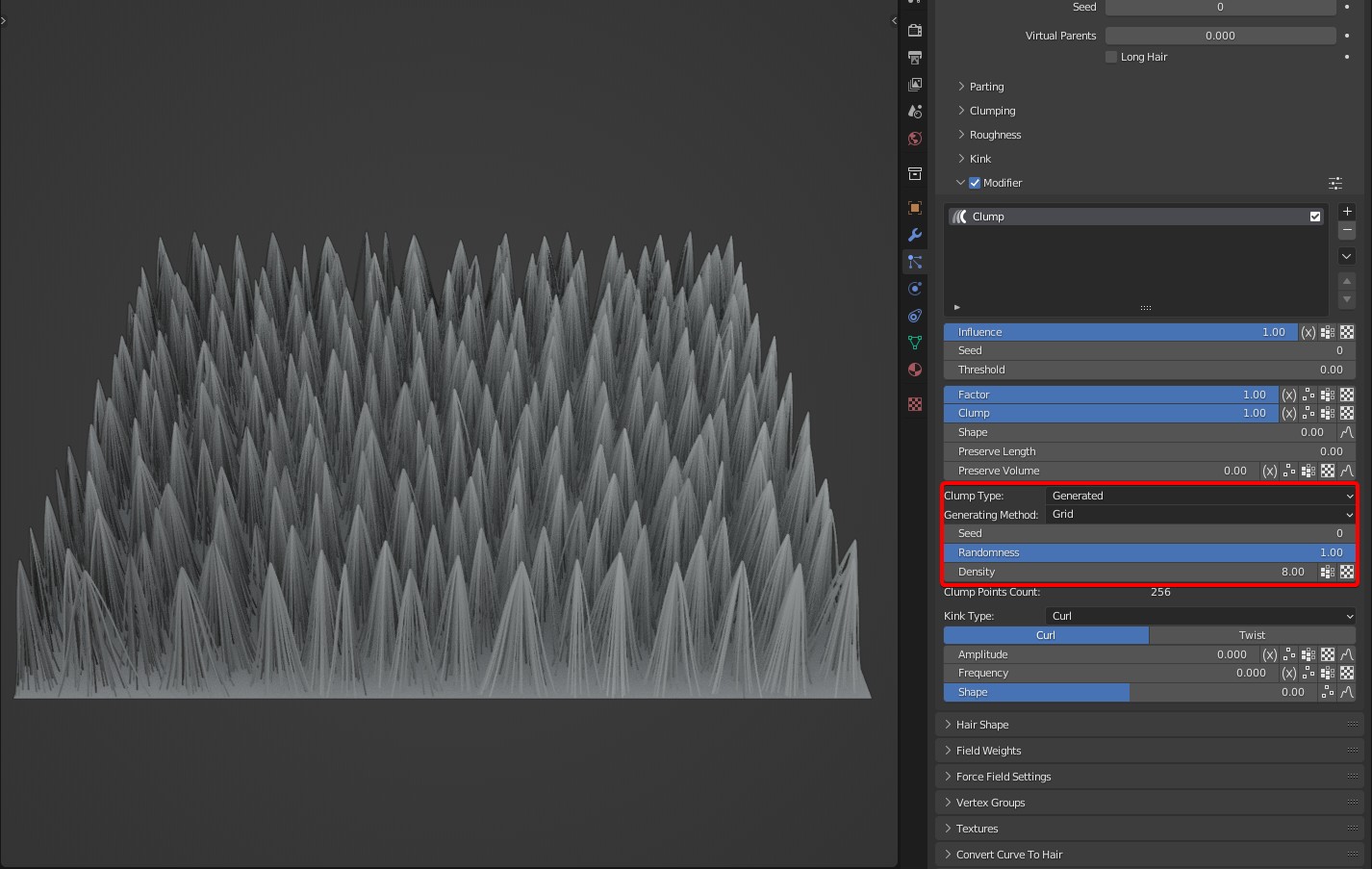
- Poisson Disk: The calculation is fast, but the distribution is uneven when clump points are few.
Seed: Randomize the position where the clumps are.
Randomness: In Grid mode, the randomness of the position of the clump points. The larger the value, the more random the result will be.
Distance Min: In 'Poisson Disk' mode, it's the minimum distance between the generated clump points. It affects the number of clump points with 'Density'.
Density: The density of clump points, the larger the value, the larger the number of clumps.
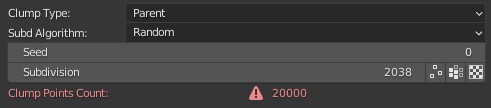
Clump Points Count: The number of generated clump points. When the number of clump points is greater than or equal to the number of hair, it will be displayed in red with a warning icon to avoid blindly increasing Density without any effect, but greatly slowing down the calculation speed;
TIP
Tip: When the number of clumps is equal to or greater than the number of hair, there is no effect because one hair forms a clump.
Clumping Kink Options
Kink Type: Many types are available.
General parameters
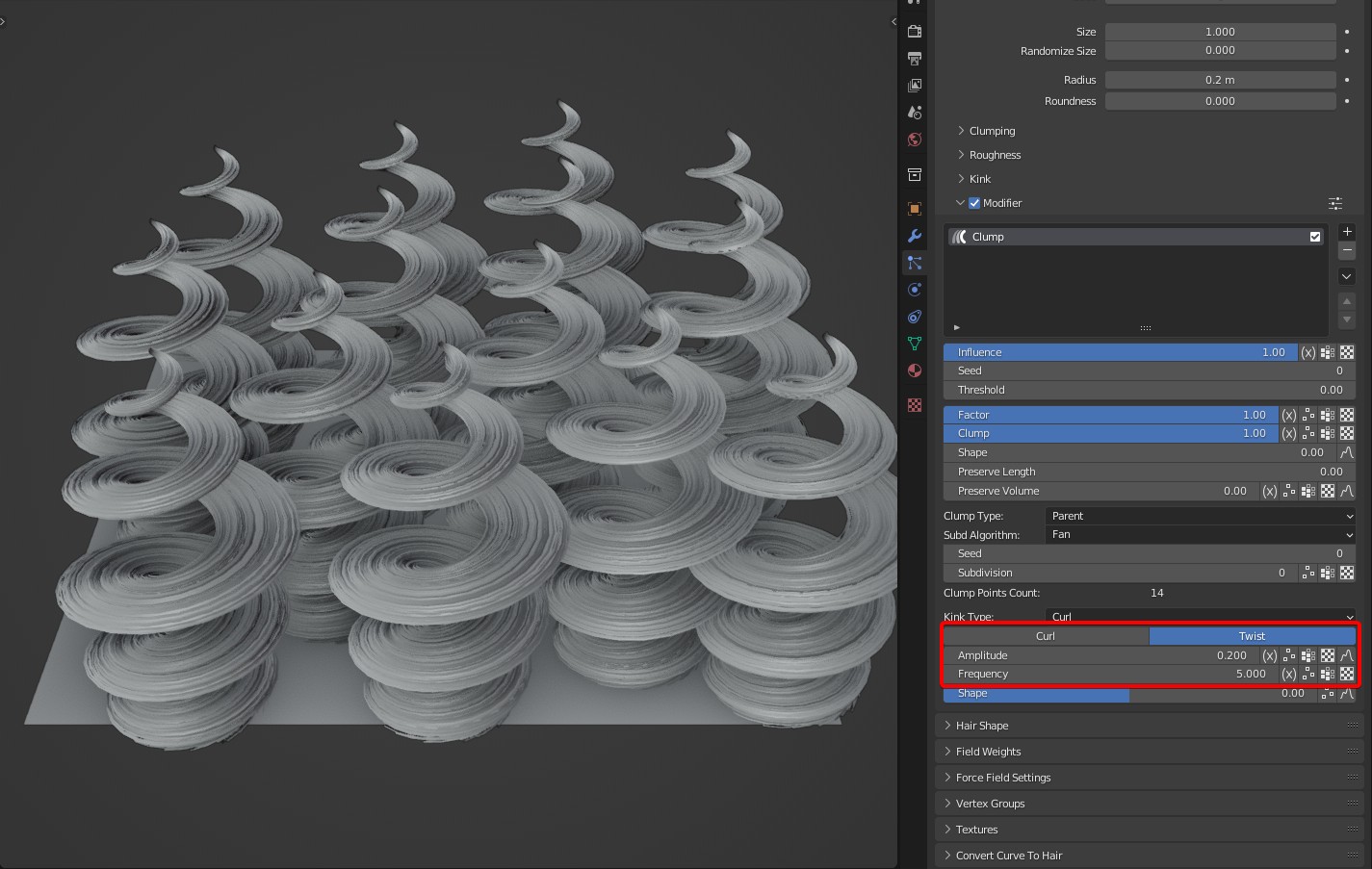
Kink Type: Curl
Two curl types are available: Curl and Twist. They work the same as those that come with Blender.
Effect comparison
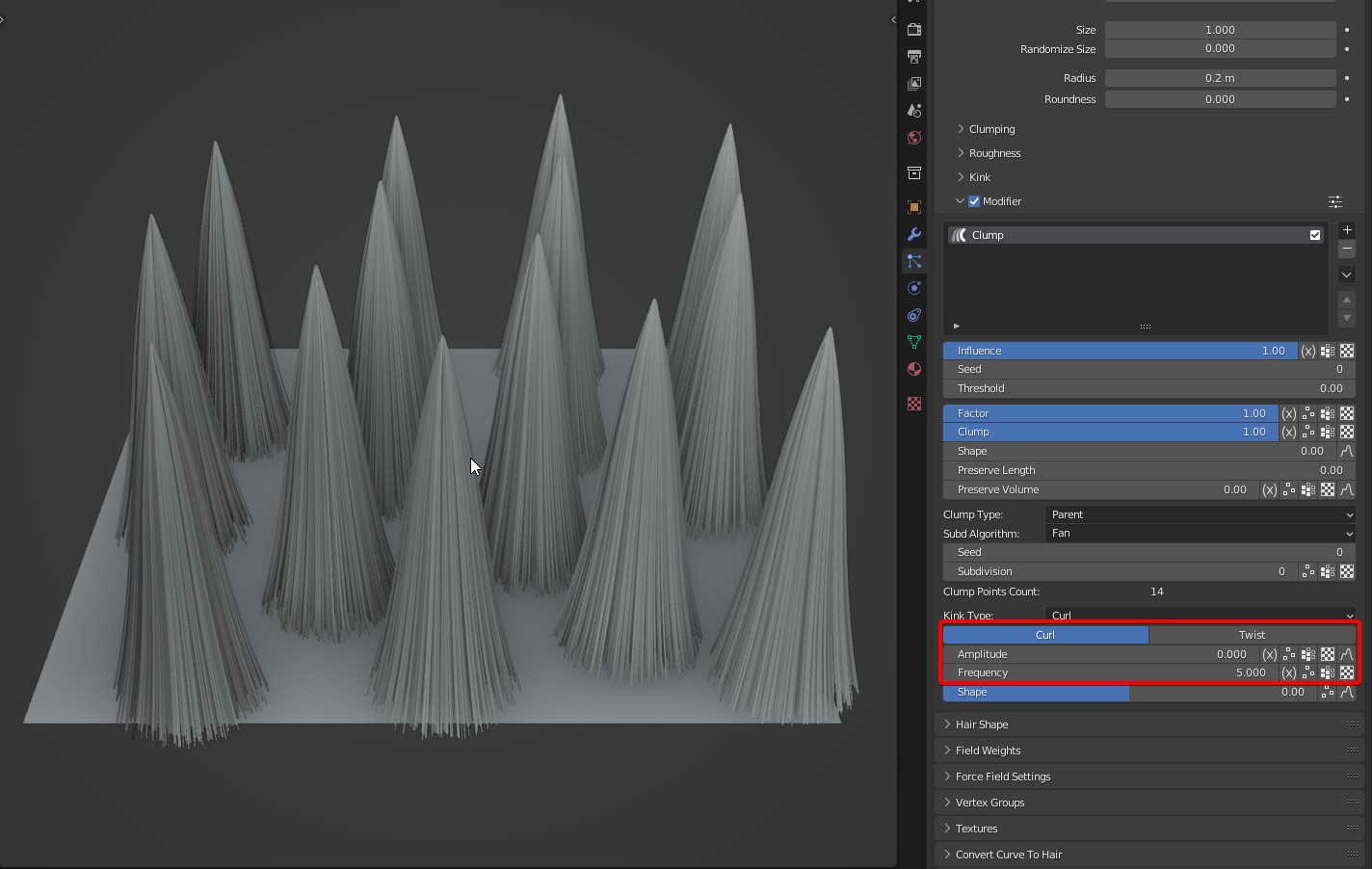
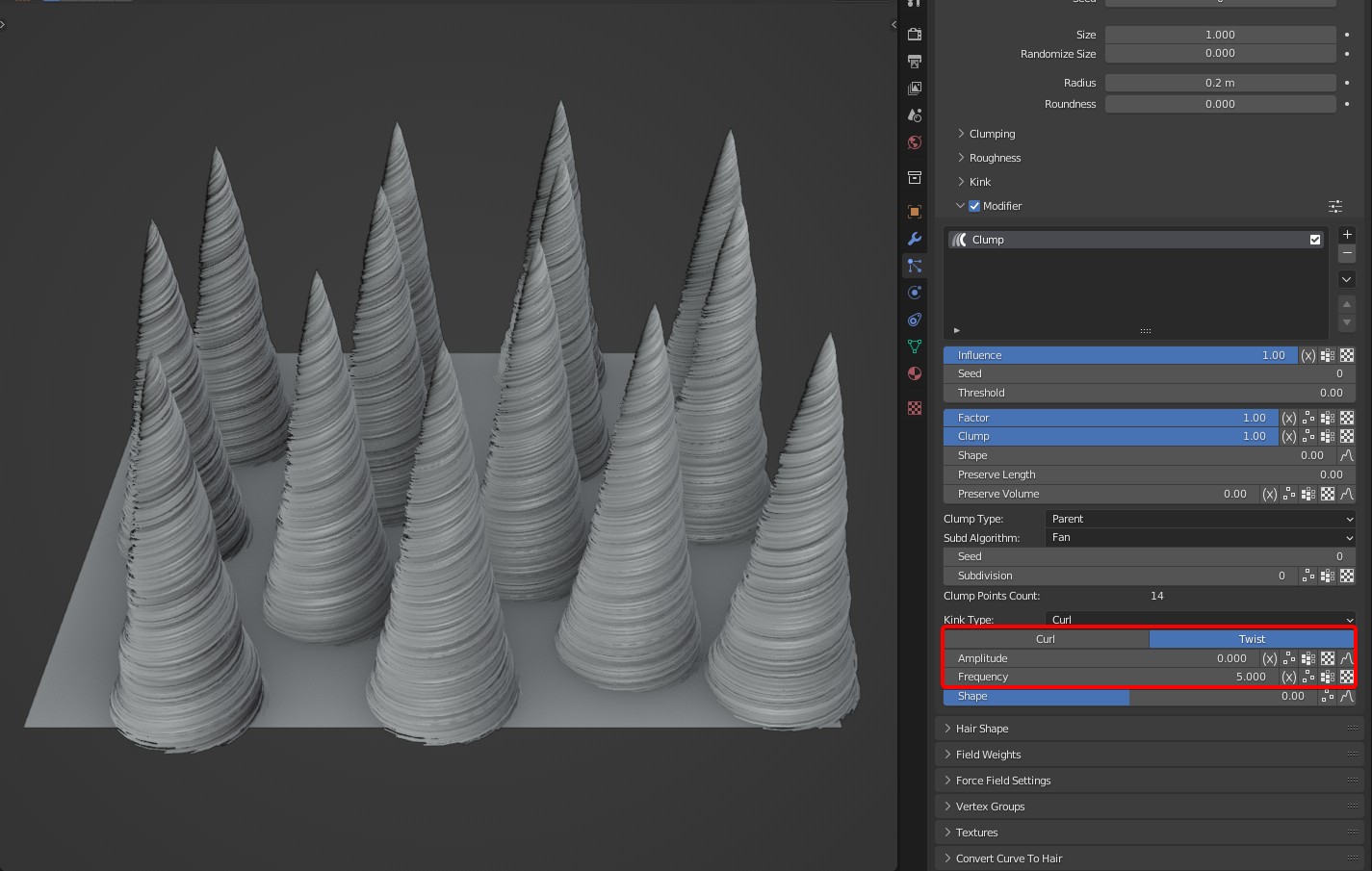
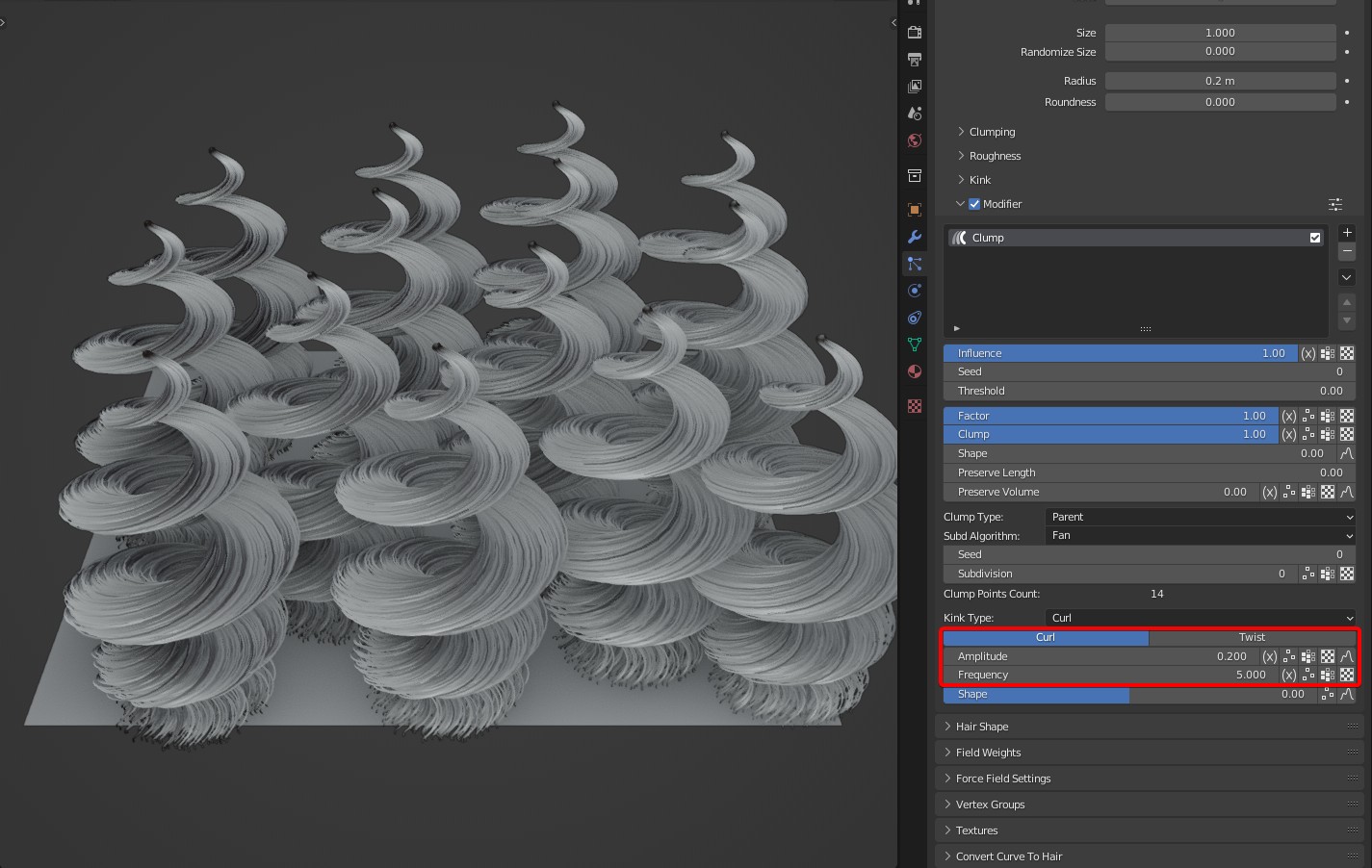
Amplitude: Controls the magnitude of the clump rotation offset. It can be controlled with a curve. By default, it's linear control from roots to tip.
Frequency: Controls the time of Kink. In Curl of kink type, the larger the Frequency is, the more the coils will be; Frequency represents the number of coils. In Wave of kink type, the larger the Frequency is, the more waves will be.
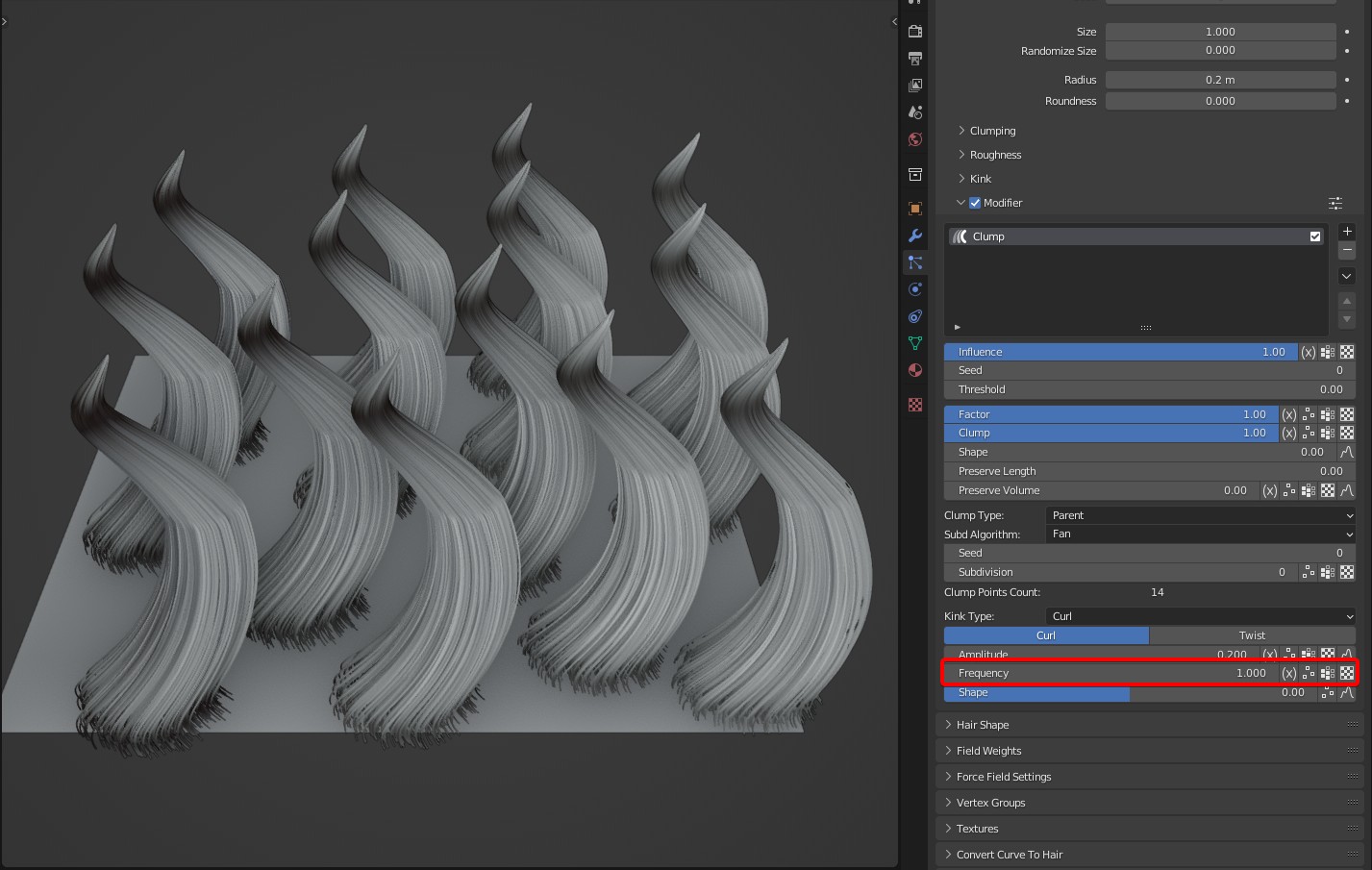
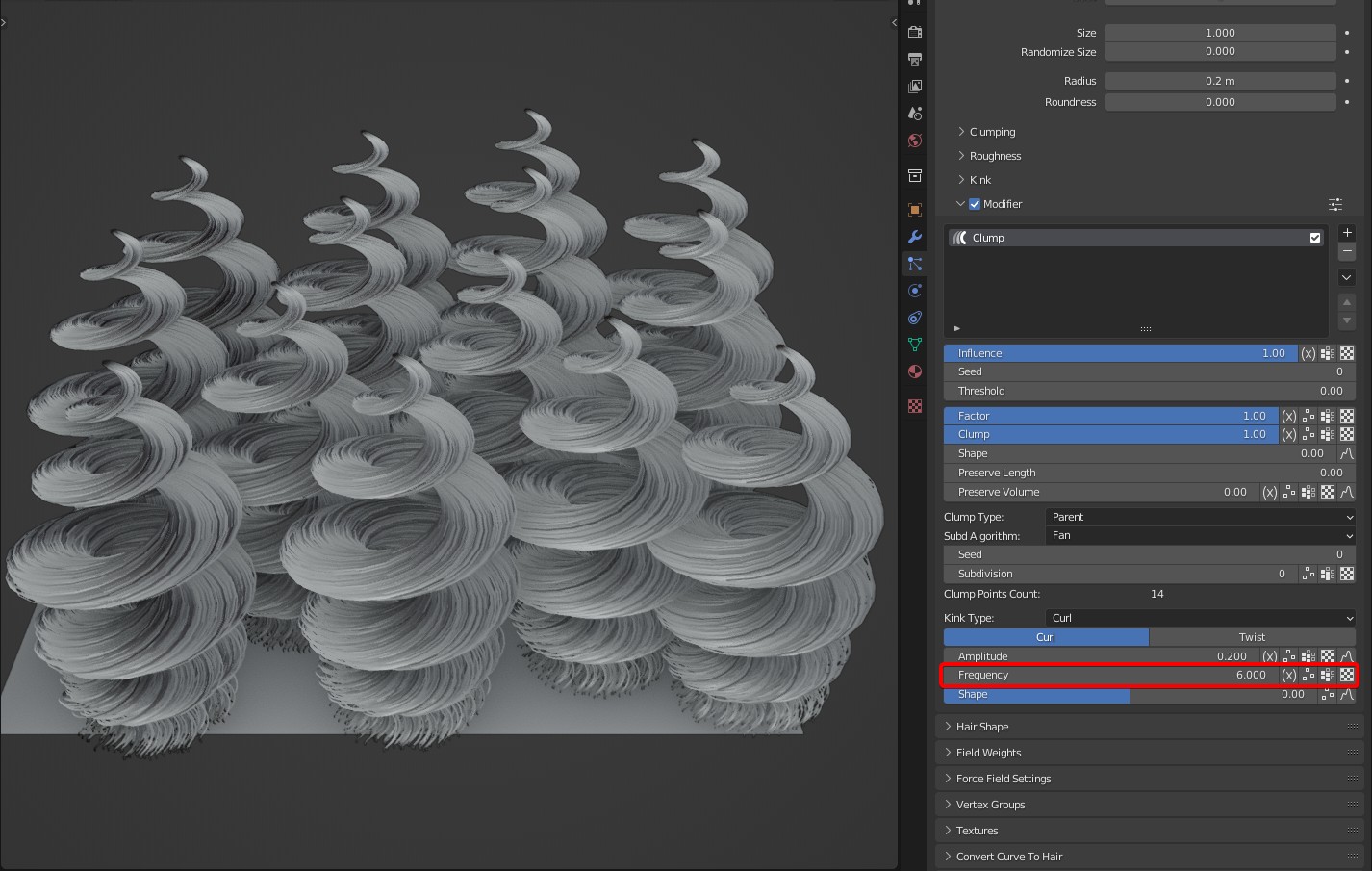
- Shape: The degree of kink from root to tip.
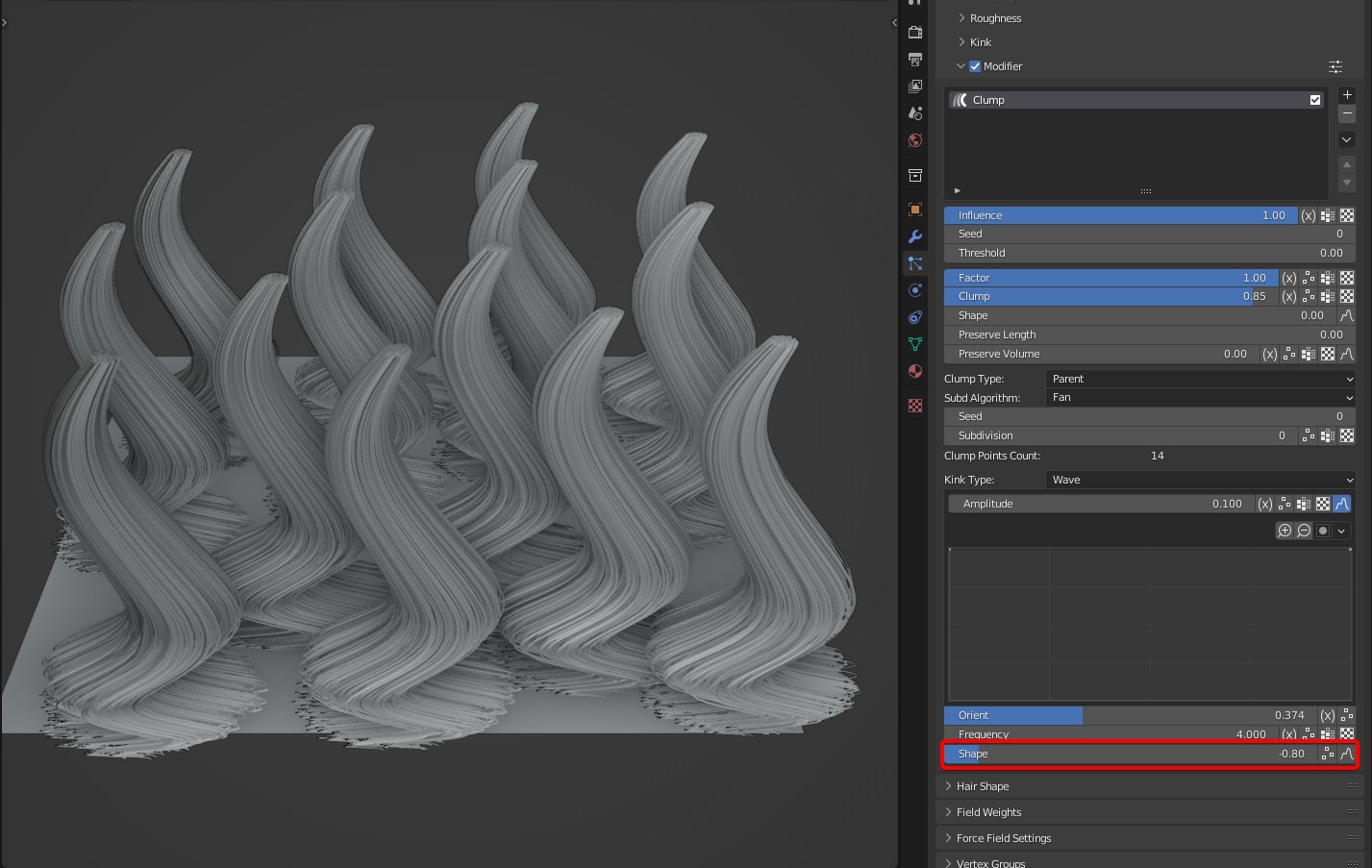
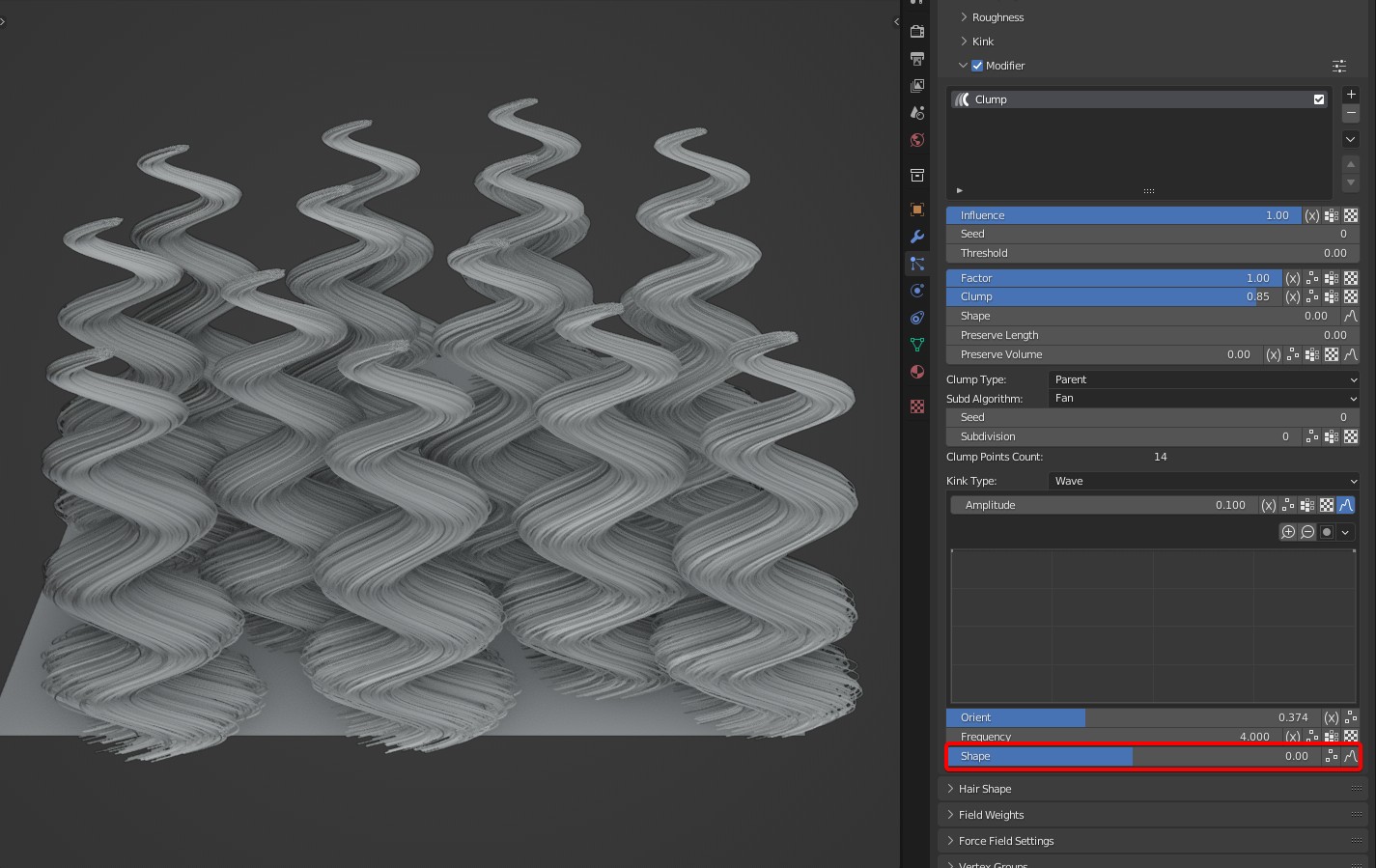
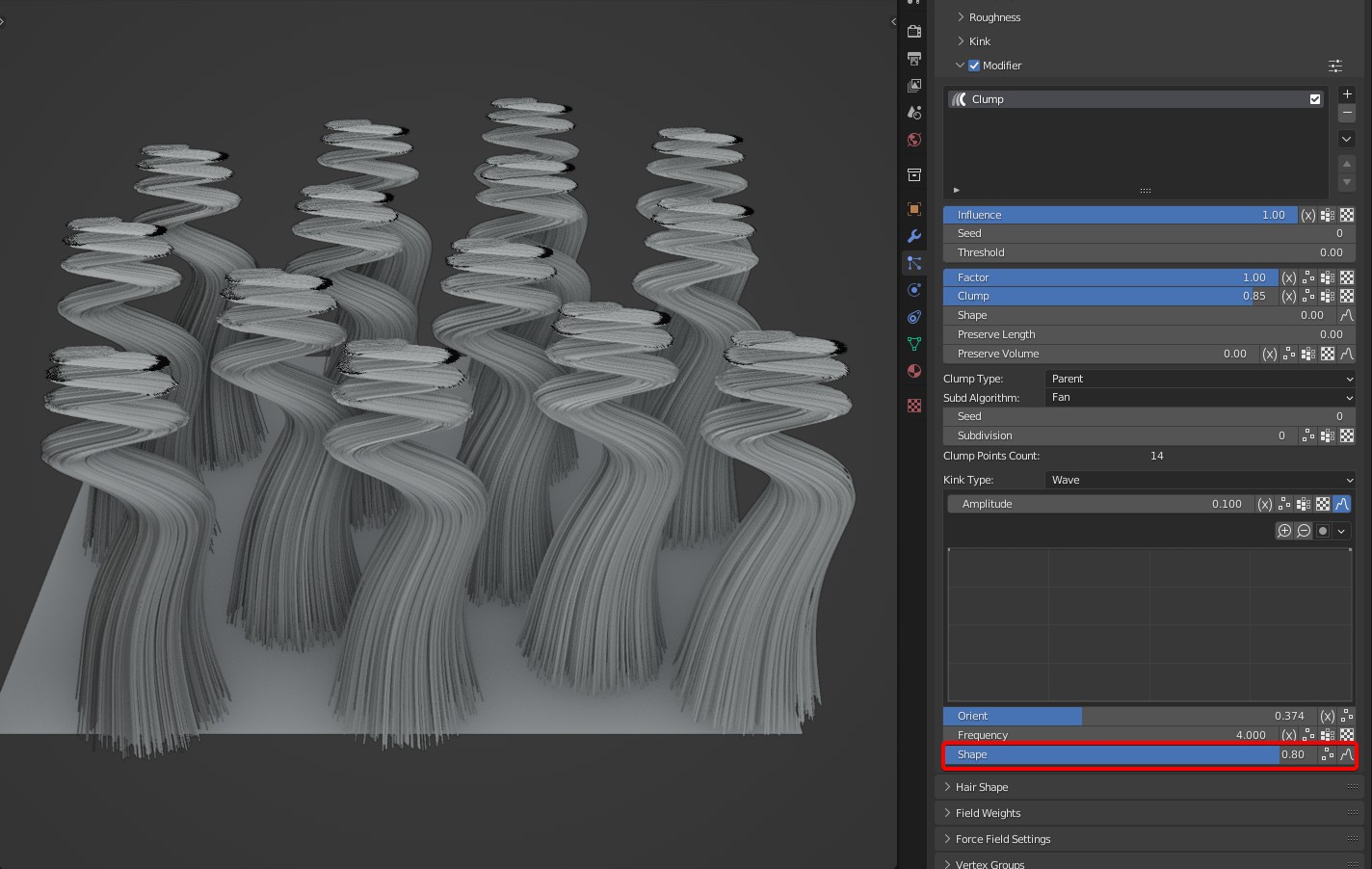
TIP
Tip: It can be controlled by a curve completely, and the value doesn't work.
Other parameters
- Orient: An option specific to Wave that controls the direction of the waves.
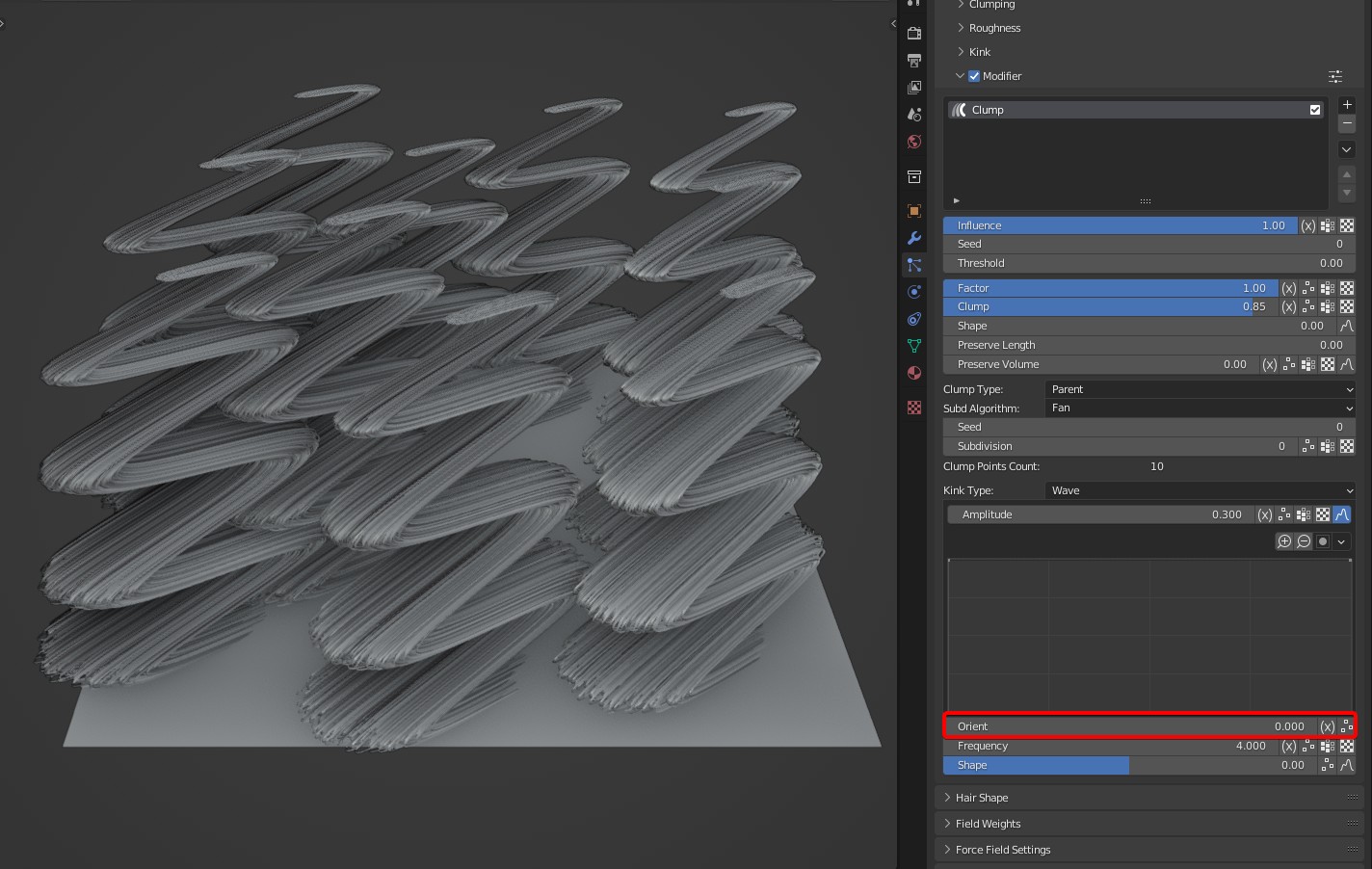
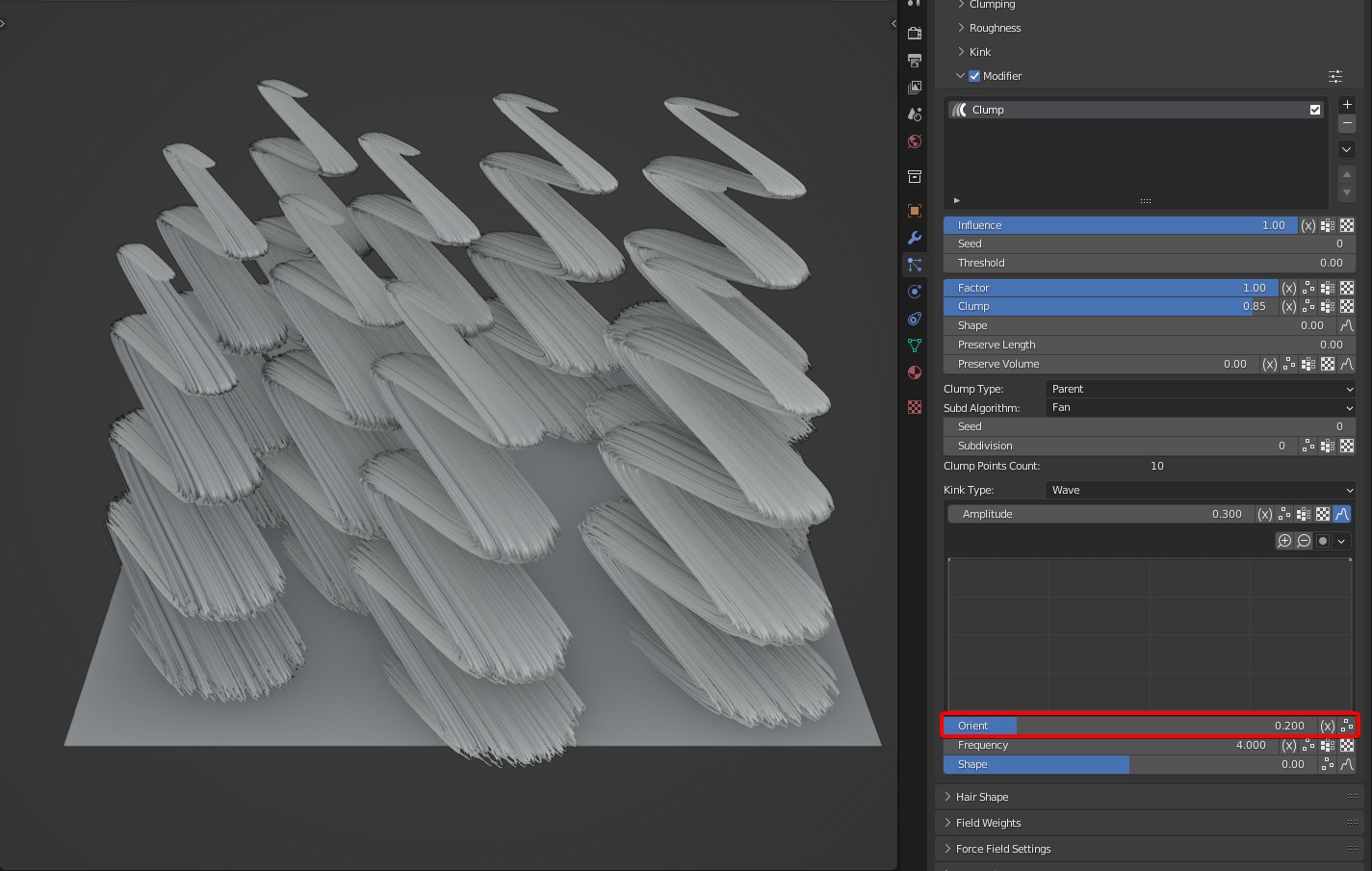
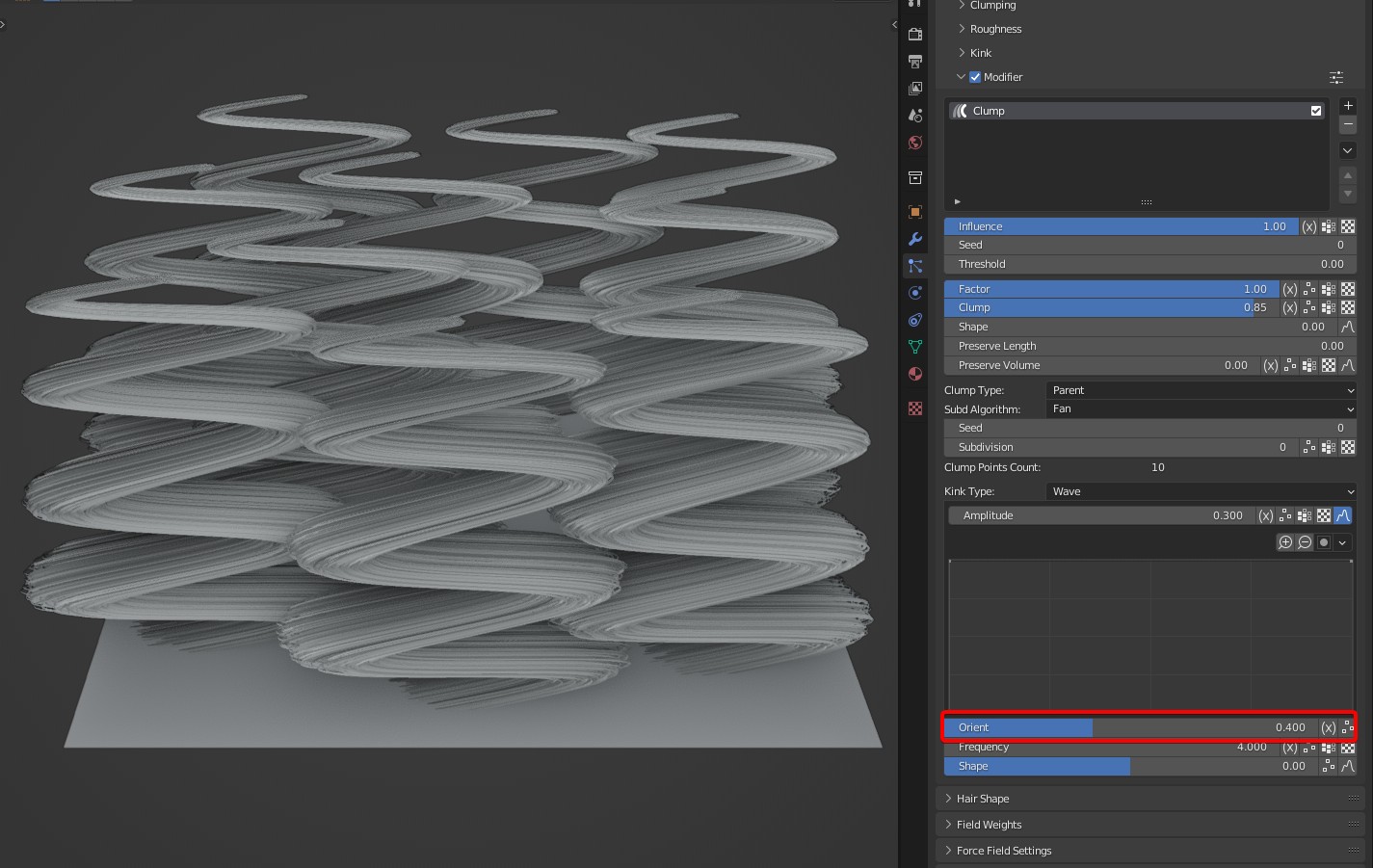
TIP
Tip: It supports randomization to get different directions of wave on the different clamps.
Case Demonstration
- Case 1
- Case 2
- Case 3
 VFX Grace
VFX Grace